How To Set Stop Loss On Options Robinhood
Options Knowledge Center
An option is a contract between a heir-apparent and a seller, and its value is derived from an underlying security. These contracts are role of a larger group of financial instruments called derivatives. On Robinhood, options contracts are traded on stocks and ETFs. Generally speaking, options are quite flexible, and they can exist used in different ways depending on a person's goals. Some people use options to hedge the risk of losses (for instance, helping protect the value of their portfolio from a downturn). Others may use options to pursue additional income by monetizing the stocks they ain. Still, it's important to note that trading options is mostly riskier than investing in stocks. When trading options, potential losses can accrue at a much faster rate, and it's possible to lose your entire initial investment (or more). Trading options requires approval on Robinhood, and information technology isn't advisable for everyone. Want to larn more before diving in? Our Options Knowledge Centre helps explain key terminology, basic and advanced trading strategies, and how to place an options trade on Robinhood.
Options are a way to actively interact with stocks you're interested in without actually trading the stocks themselves. When you trade options, y'all can control shares of stock without ever having to ain them.
With options, an investor can magnify their potential gains or losses, relative to their initial investment. This is known as leverage. When a person buys an pick, they gain exposure to the movement of a stock, and that contract represents a potential trade of 100 shares (that is, without the investor necessarily owning the underlying shares at whatsoever point in time). Equally a result, even modest changes in a stock cost—up or down—can have a dramatic effect on the value of an options position. Leverage can provide the opportunity for outsized gains, while exposing an investor to outsized losses. Leverage is function of what makes options strategies risky.
The enquire price is the amount of money sellers in the market are willing to receive for an options contract. The ask price will always be college than the bid price.
The bid price is the corporeality of coin buyers in the market are willing to pay for an options contract. The bid price will always be lower than the inquire price.
The strike price of an options contract is the cost at which the options contract tin can be exercised. Remember of the strike price as the anchor of your contract: If yous're buying a call, your call is profitable if the value of the stock goes above the strike cost (plus whatever premium yous paid). If the value of the stock stays below your strike price, your options contract will elapse worthless. Remember, you're not actually buying shares of the stock unless you exercise your contract. This is because the contract gives yous the choice to buy the bodily shares of the stock at the strike price.
Buying and Selling an Options Contract
Options can exist catchy, so it's important to know exactly how the actions you take will get you closer to your goal:
The owner of an options contract has the right to practice the contract, let information technology expire worthless, or sell it back into the market place before expiration. The owner of the contract is likely to exercise the contract if information technology's "in the money." On the other hand, the person who sold the contract to collect the premium is assigned when the owner of the contract exercises it. For more information on exercise and assignment, check out our article Exercise, Assignment, & Expiration.
Since the owner has the right to either do the contract or allow it just expire worthless, she pays the premium–the per-share price for property the contract–to the seller. As a buyer, yous can think of the premium as the price to purchase the pick. If you buy or sell an choice earlier expiration, the premium is the price it trades for. Yous can merchandise the option in the marketplace like to how you'd merchandise a stock. The premium is not arbitrary, as it'southward tied to the value of the contract and the underlying security. The underlying stock's price, the underlying stock'south volatility, and the amount of fourth dimension left until expiration all influence an option'southward premium.
Liquidity refers to the ability for a trader to open or shut an selection position at a given price and fourth dimension. This is based on supply and demand in the marketplace. Low liquidity tin hinder or prevent a trader from beingness able to buy or sell a contract. For case, if there isn't a heir-apparent interested in purchasing an options contract you'd similar to sell at a specific toll, y'all may non be able to sell the contract when you'd like to, which tin affect your potential gains or losses.
Owners of call options generally expect the stock to increment in value, while sellers of telephone call options generally look the stock'south value to decrease or remain the same. Ownership a call option gives yous the right, but non the obligation, to purchase 100 shares of the underlying stock at the designated strike price. The value of a telephone call option tends to appreciate as the value of the underlying stock increases. Selling a call selection allows you to collect the premium while obligating you to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock to the owner at the agreed-upon strike price if the owner of the contract chooses to exercise the contract.
Example
What if you call back the price of the stock is going up? In this example you'd buy to open a call position. Buying a call gives you lot the right to buy the underlying stocks from the option seller for the agreed-upon strike toll. From there, you can sell the stocks back into the market at their current market value if you and then choose. For instance, you recollect MEOW's upcoming product release is going to ship the price of the stock soaring, so you buy a call for MEOW at a $ten strike price with a $1 premium (the price of the contract) expiring in a calendar month. Allow's break that down. Symbol: MEOW Expiration: A month from now Strike Price: $10 Premium: $1 The product release gave the stock a bump, and the day your contract expires, MEOW hits $15. Great! This ways you can sell the contract in the market for at least $5 and earn at least a $4 profit per share. The reason the contract is worth at least $5 is that you could practise the contract to buy the shares at $10, then sell the stocks in the market at their current trading price of $fifteen. You'd earn $4 per share if you exercised the contract instead of selling it.
Owners of put options more often than not look the stock to decrease in value, while sellers of put options generally expect the stock's value to increase or remain the same. Buying a put option gives you the right, just non the obligation, to sell 100 shares of the underlying stock at the designated strike cost. The value of a put option tends to capeesh equally the value of the underlying stock decreases. Selling a put option allows you lot to collect the premium, while obligating you to purchase 100 shares of the underlying stock from the possessor at the agreed-upon strike price if the owner of the contract chooses to exercise the contract.
Example
What if yous call up the price of the stock is going down? In this example, yous could buy to open up a put choice. Buying a put gives you the right to sell the underlying stock back to the selection seller for the agreed-upon strike price if you lot so cull. For example, you think MEOW's upcoming earnings call is going to tank the price of the stock, so yous buy 1 MEOW put selection expiring in a week with a strike price of $10 for a premium (the toll of the contract) of $ii. Let's suspension that down. Symbol: MEOW Expiration: A week from now Strike Price: $x Premium: $2 Your prediction is correct, and within the calendar week MEOW is trading at $6. Your put option is now worth at least $4, and then you lot can sell it in the market for a profit (less the toll of your $two premium). You've simply made $200 on MEOW's subtract in value.
Knowing When to Purchase or Sell
When opening a position, you tin either buy a contract with the intention of exercising it when it reaches its strike price, or you can sell a contract to collect the premium and hope to not be assigned. Buying an options contract makes you the owner/holder of the contract, and in render for paying the premium, you have the right to choose to either do the contract, let information technology expire worthless, or sell it back into the market place earlier expiration. The seller of an options contract collects the premium paid past the buyer, but is obligated to buy or sell the agreed-upon shares of the underlying stock if the owner of the contract chooses to exercise the contract. 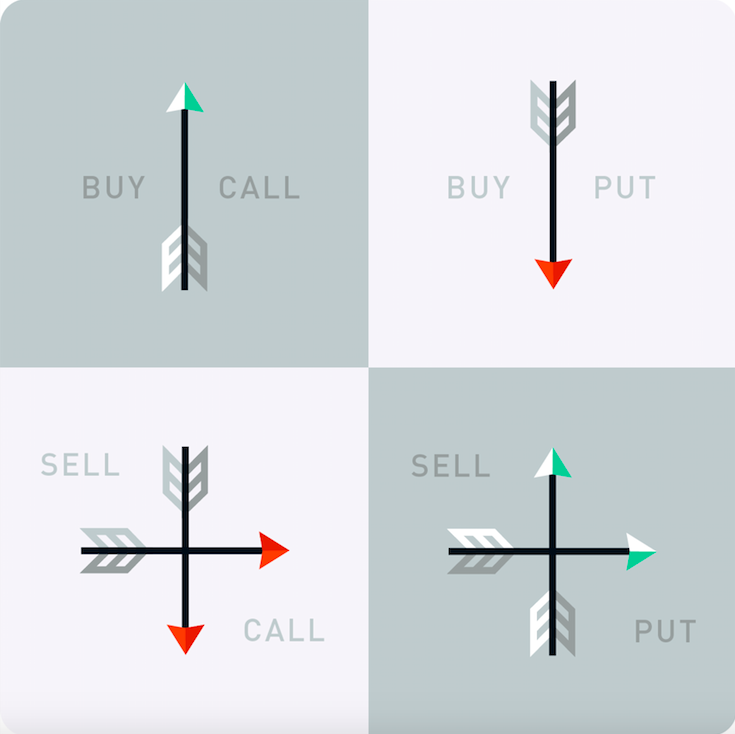
The owner has the right to exercise the contract or not, whereas the seller has the obligation to make good on the contract if she'south assigned. When the owner of the contract exercises it, the seller is assigned.
The closer an choice is to expiring, the less fourth dimension value the choice volition accept. The further away a contract is from its expiration appointment, the more than potential at that place is for price movement, which generally would make the contract trade at a college price.
The suspension-even point of an options contract is the bespeak at which the contract would be price-neutral if the owner were to exercise it. It'due south of import to consider the premium paid for the contract in addition to the strike price when calculating the break-even signal.
It'southward important to besides continue in heed that contracts are typically for 100-share blocks. In the above instance, you'd be entitled to purchase 100 shares of MEOW at the agreed-upon strike toll. All contracts on Robinhood are for 100 shares. Though options contracts typically stand for 100 shares, the price of the option is shown on a per-share ground, which is the industry standard.
Options Levels on Robinhood
Depending on your feel and other factors, you might be eligible for unlike levels of options trading on Robinhood. With Level 2 approval, you lot'd have access to the following strategies: With Level 3 approval, you'd have admission to everything available with Level 2 approving and the post-obit strategies: You tin discover deeper dives on our Basics Options Strategies (Level ii) and Advanced Options Strategies (Level 3). Information technology'due south helpful to annotation that Robinhood doesn't allow selling uncovered options, because in that location's no limit to the amount of money you could lose with some strategies.
Disclosures
Disclosures
Options trading entails significant run a risk and is non appropriate for all investors. Certain complex options strategies behave boosted risk. Robinhood Financial does not guarantee favorable investment outcomes and there is always the potential of losing money when you invest in securities, or other financial products. Investors should consider their investment objectives and risks carefully before investing. To learn more near the risks associated with options, please read the Characteristics and Risks of Standardized Options before you lot begin trading options. Delight also be aware of the risks listed in the following documents: 24-hour interval Trading Risk Disclosure Statement and FINRA Investor Information. Examples independent in this article are for illustrative purposes only. Supporting documentation for whatsoever claims, if applicable, will exist furnished upon request.
Reference No. 1392734
Source: https://robinhood.com/us/en/support/articles/options-knowledge-center/?region=US

0 Response to "How To Set Stop Loss On Options Robinhood"
Post a Comment